
The views expressed in the project do not necessarily reflect the views of The Office for Learning and Teaching. Support for this project website has been provided by The Office for Learning and Teaching, which is part of the Department of Industry, Innovation, Science, Research and Tertiary Education. Single slit diffraction, diffraction gratings.ĭownloads (thumbnails at 50% of size of animation) Recreating a hologram: coherence beam and hologram plate. X-ray diffraction.įorming a hologram: beam splitter, object and reference beams, interference at the film. Diffraction of monochromatic light results in a bright central band on the screen as the result of constructive interference, other bright bands are placed on.

Diffraction requires wavelengths less than 0.1 nm. The atomic lattice as a diffraction grating. When is the eye diffraction limited? The resolution of telescopes. when light beams hit apertures or other kinds of structures leading to spatially dependent. Resolving two point sources: Rayleigh's criterion. Various kinds of diffraction effects can be observed e.g. Diffraction pattern from a circular aperture. Rayleigh criterion and the Airy disc: Aperture and resolutionĬircular apertures in optics. A modern recreation of Arago's experiment. The bright dot at the centre of the shadow: Poisson's argument against the wave nature of light. The hydrogen spectrum and the origins of quantum mechanics. Continuous spectra and line spectra, absorption and emission spectra. Hence, the modification introduced by diffraction optics is due to the more accurate propagation of the field from the exit pupil to the focal region. Analyzing the interference pattern and equations explains the observed phenomena with light passing through double-slits. In diffraction optics we compute the field in the focal region using diffraction integrals instead of using ray tracing. (a) Light passing through is diffracted in a pattern similar to a double slit, with. Young's experiment with finite slit width: I q shows both interference and diffraction effects.Ī light-hearted discussion to illustrate why we don't notice quantum interference in everyday life.Īdding phasors with 2, 3, 4 and many slits: Diffraction gratings. Double-slit diffraction is the observed outcome where light passing through two slits produces beams that interact with each other. A diffraction grating is a large number of evenly spaced parallel slits. Young's experiment with finite slits.ĭiffraction from a single slit:Huygens' construction.
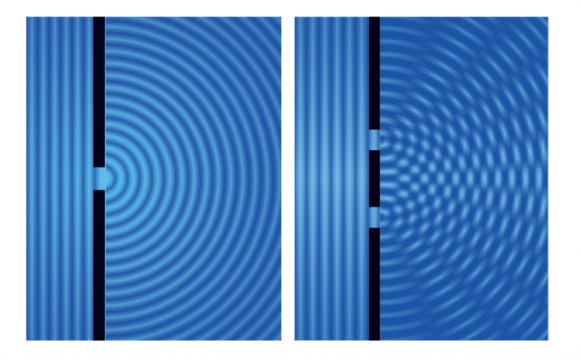
X-ray, neutron and electron diffractionĭiffraction from a single slit. Shadows and beams with water waves of short wavelength. Diffraction, shadows, beams, Huygens' construction.ĭiffraction of light and sound.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
